Traffic types and iptables rules in Istio sidecar explained
Istio uses iptables for traffic hijacking, and there is one rule chain named ISTIO_OUTPUT which contains the following rules.

Tetrate offers an enterprise-ready, 100% upstream distribution of Istio, Tetrate Istio Subscription (TIS). TIS is the easiest way to get started with Istio for production use cases. TIS+, a hosted Day 2 operations solution for Istio, adds a global service registry, unified Istio metrics dashboard, and self-service troubleshooting.
Istio uses iptables for traffic hijacking, and there is one rule chain named ISTIO_OUTPUT which contains the following rules.
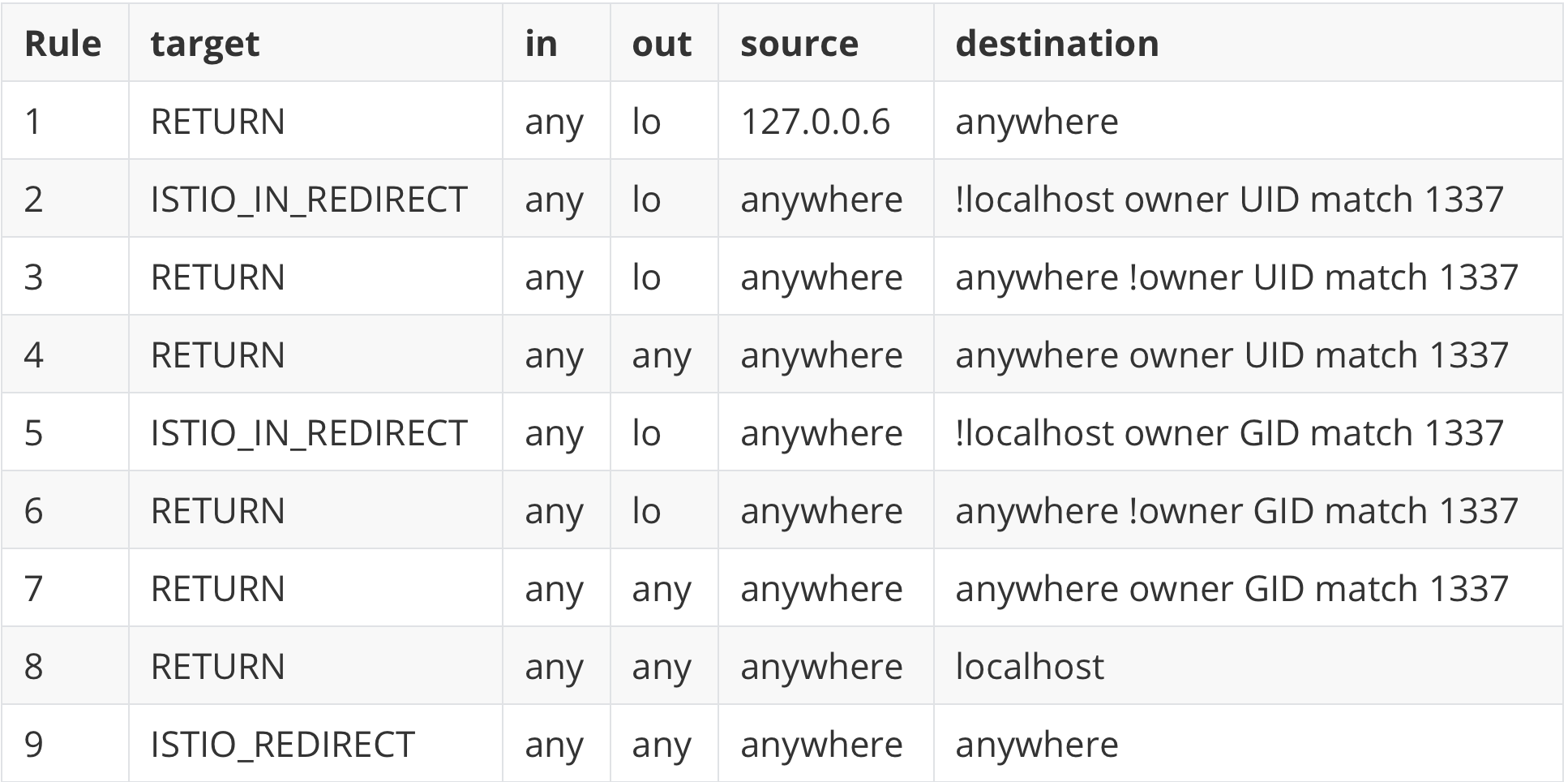

ISTIO_OUTPUT rule chain
The sidecar applies these rules to deal with different types of traffic. This article will show you the six types of traffic and their iptables rules in Istio sidecar.
iptables Traffic Routing in Sidecar
The following list summarizes the six types of traffic in Sidecar.
- Remote service accessing local service: Remote Pod -> Local Pod
- Local service accessing remote service: Local Pod -> Remote Pod
- Prometheus crawling metrics of local services: Prometheus -> Local Pod
- Traffic between Local Pod services: Local Pod -> Local Pod
- Inter-process TCP traffic within Envoy
- Sidecar to Istiod traffic
The following will explain the iptables routing rules within Sidecar for each scenario, which specifies which rule in ISTIO_OUTPUT is used for routing.
Type 1: Remote Pod -> Local Pod
The following are the iptables rules for remote services, applications, or clients accessing the local pod IP of the data plane.
Remote Pod -> RREROUTING -> ISTIO\_INBOUND -> ISTIO\_IN\_REDIRECT -> Envoy 15006 (Inbound) -> OUTPUT -> **ISTIO\_OUTPUT** **RULE 1** -> POSTROUTING -> Local Pod
We see that the traffic only passes through the Envoy 15006 Inbound port once. The following diagram shows this scenario of the iptables rules.

Type 2: Local Pod -> Remote Pod
The following are the iptables rules that the local pod IP goes through to access the remote service.
Local Pod-> OUTPUT -> ISTIO_OUTPUT RULE 9 -> ISTIO_REDIRECT -> Envoy 15001 (Outbound) -> OUTPUT -> ISTIO_OUTPUT RULE 4 -> POSTROUTING -> Remote Pod
We see that the traffic only goes through the Envoy 15001 Outbound port.
The traffic in both scenarios above passes through Envoy only once because only one scenario occurs in that Pod, sending or receiving requests.

Type 3: Prometheus -> Local Pod
Prometheus traffic that grabs data plane metrics does not have to go through the Envoy proxy.
These traffic flows pass through the following iptables rules.
Prometheus-> RREROUTING -> ISTIO_INBOUND (traffic destined for ports 15002, 15090 will go to INPUT) -> INPUT -> OUTPUT -> ISTIO_OUTPUT RULE 3 -> POSTROUTING -> Local Pod

Type 4: Local Pod -> Local Pod
A Pod may simultaneously have two or more services. If the Local Pod accesses a service on the current Pod, the traffic will go through Envoy 15001 and Envoy 15006 ports to reach the service port of the Local Pod.
The iptables rules for this traffic are as follows.
Local Pod-> OUTPUT -> **ISTIO\_OUTPUT** **RULE 9** -> ISTIO\_REDIRECT -> Envoy 15001(Outbound)-> OUTPUT -> **ISTIO\_OUTPUT** **RULE 2** -> ISTIO\_IN\_REDIRECT -> Envoy 15006(Inbound)-> OUTPUT -> **ISTIO\_OUTPUT** **RULE 1** -> POSTROUTING -> Local Pod

Type 5: Inter-process TCP traffic within Envoy
Envoy internal processes with UID and GID 1337 will communicate with each other using lo NICs and localhost domains.
The iptables rules that these flows pass through are as follows.
Envoy process (Localhost) -> OUTPUT -> **ISTIO\_OUTPUT** **RULE 8** -> POSTROUTING -> Envoy process (Localhost)

Type 6: Sidecar to Istiod traffic
Sidecar needs access to Istiod to synchronize its configuration so that Envoy will have traffic sent to Istiod.
The iptables rules that this traffic passes through are as follows.
pilot-agent process -> OUTPUT -> **Istio\_OUTPUT** **RULE 9** -> Envoy 15001 (Outbound Handler) -> OUTPUT -> **ISTIO\_OUTPUT** **RULE 4** -> POSTROUTING -> Istiod

Summary
In this article, you learned about the types of traffic in Sidecar, which will help you troubleshoot. In my next blog, I will take you through the ports of each component in Envoy and their functions to have a more comprehensive understanding of the traffic in Istio.










