Simplifying Service Mesh Configuration with Tetrate Service Bridge, Flux CD and GitOps
Introduction In the dynamic environment of cloud-native applications and microservices, efficiently managing service mesh configurations has become cr

Introduction
In the dynamic environment of cloud-native applications and microservices, efficiently managing service mesh configurations has become critical. Organizations need robust solutions to streamline the management and deployment of their service mesh environments. This article explores how integrating Tetrate Service Bridge (TSB) with continuous delivery tooling like Flux CD in a GitOps practice can simplify service mesh configuration and promote efficient application deployment.
TSB, GitOps and Flux CD: a Winning Combination
GitOps has gained significant traction as an operational model for managing infrastructure and application configurations, using Git as a single source of truth. Flux CD is a popular open source GitOps tool that provides continuous delivery and automated deployment capabilities for Kubernetes environments. Tetrate Service Bridge —Tetrate’s application networking and security platform—serves as a global service mesh management plane, offering organizations a powerful solution for managing their service mesh configurations across multiple environments, clouds and on-premises.
Together, Tetrate Service Bridge, FluxCD and GitOps practices allow organizations to streamline service mesh management, ensuring efficient and reliable deployment of their cloud-native applications with improved visibility, consistency and automation.
GitOps with FluxCD: a Declarative Approach
GitOps simplifies infrastructure and application management by following a declarative approach. It treats infrastructure and application configurations as code, stored in a Git repository. FluxCD, as a GitOps tool, facilitates this process by continuously monitoring the Git repository for changes to update the desired state of the Kubernetes cluster.
FluxCD’s automated synchronization capabilities ensure that any changes made to the desired state in the Git repository are automatically applied to the Kubernetes cluster. By leveraging Kubernetes controllers, FluxCD manages the deployment, updating and deletion of Kubernetes resources based on the configuration changes. This allows for efficient continuous deployment practices, enabling organizations to deliver applications rapidly and reliably.
Integrating FluxCD with Tetrate Service Bridge: Simplifying Service Mesh Configuration
Tetrate Service Bridge complements the GitOps workflow by providing a global management plane for multiple service mesh environments. Tetrate’s management plane simplifies configuration and security of distributed services giving teams centralized configuration and policy authorship with consistent and auditable application of those policies across heterogeneous environments. With TSB’s GitOps support, application teams can create TSB configuration resources directly within their application clusters, pushing changes alongside application updates in the same manner.
GitOps Pull and Push Approaches
There are two deployment strategies for GitOps: push-based and pull-based.
In the push approach, once a commit has been made on a Git repository or a CI pipeline was executed successfully, an external system (mostly CD pipelines) is triggered to deploy the artifacts to the cluster. In this approach, the pipeline system requires the relevant permissions to access the cluster.
On the other hand, in the pull approach, an agent inside the destination cluster regularly scans the associated Git repositories. If a change is detected, the cluster state will be updated from inside the cluster. This means that the CD components are moved to reside within the clusters themselves.
Choosing between the push and pull approaches depends on the specific needs and requirements of your team or organization. There is no one-size-fits-all solution, as each scenario varies greatly. It is important to weigh the needs of your team or organization and consider the pros and cons of each approach. In some cases, a combination of both push and pull approaches may be the most suitable solution.
FluxCD and Tetrate Service Bridge support both push and pull GitOps strategies, depending on requirements. FluxCD can be used to trigger deployments in the push approach, where external systems handle the deployment process. Alternatively, in the pull approach, FluxCD can act as the agent within the cluster, scanning the Git repositories and updating the cluster state accordingly.
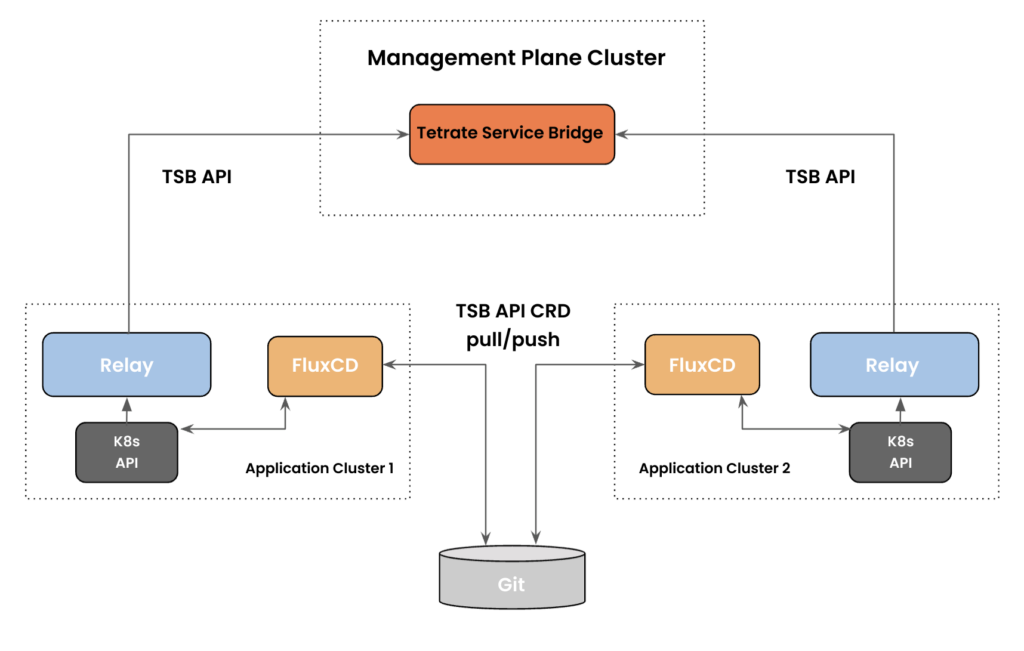

The Power of GitOps, FluxCD and TSB Integration
Unified configuration management. GitOps enables a unified approach to managing both application and service mesh configurations. By defining and managing all configuration changes in a single Git repository, teams ensure consistency and traceability across their infrastructure and application stack.
Automation and continuous deployment. GitOps, FluxCD and TSB together provide end-to-end automation of service mesh configurations. Changes made to the Git repository trigger automated reconciliation processes, ensuring that the service mesh’s actual state aligns with the desired state defined in the repository. This promotes continuous deployment practices, accelerates application delivery and reduces the risk of configuration drift.
Collaboration and review. GitOps workflows promote collaboration and review processes for service mesh configuration management. Teams can leverage Git’s pull request, code review and approval mechanisms to validate and review changes before they are applied to the cluster. This fosters collaboration among team members, improves the overall quality of configurations and ensures adherence to best practices.
Scalability and consistency. With GitOps, FluxCD and TSB, organizations can efficiently manage multiple clusters and environments. Using branches or paths within the Git repository, teams can define environment-specific configurations, ensuring each environment has its appropriate settings while maintaining consistency across deployments.
Demo: Configuring Flux CD for GitOps
In this section, we will explore how to configure Flux CD with GitHub integration to deploy a test application to a target cluster with all the necessary TSB resources.
Step 1: Cluster Setup
Before we dive into configuring Flux CD, let’s set up the target cluster with a GitHub integration. Make sure you have the following prerequisites:
- Flux installed
- TSB is up and running, and GitOps has been enabled for the target cluster
- GitHub personal access token with repo permissions. See the GitHub documentation on creating a personal access token.
Step 1.1. Export your credentials:
export GITHUB_USER=<your-username>Step 1.2. Check you have everything needed to run Flux by running the following command:
flux check --pre
► checking prerequisites
✔ Kubernetes 1.23.17-eks-c12679a >=1.20.6-0
✔ prerequisites checks passedStep 1.3. Install Flux on the target cluster with GitHub integration, use the following command under the target cluster Kubernetes context:
flux bootstrap github \
--owner=$GITHUB_USER \
--repository=fleet-infra \
--branch=main \
--path=./clusters/my-clusterNote:You will need a GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT) to input in the above command. If you’re using your personal GitHub account for testing purposes, add the --personal --private flags.
The bootstrap command above does the following:
- Creates a Git repository
fleet-infraon your GitHub account (your value fromexport GITHUB_USER=<your-username>) - Adds Flux component manifests to the repository
- Deploys Flux Components to your Kubernetes Cluster
- Configures Flux components to track the path
/clusters/my-clusterin the repository
Under the hood, Flux CD uses a Kustomization with a GitRepository source to store its own resources. You can query the status of Flux using the following command:
flux get all
NAME REVISION SUSPENDED READY MESSAGE
gitrepository/flux-system main@sha1:80299a36 False True stored artifact for revision 'main@sha1:80299a36'
NAME REVISION SUSPENDED READY MESSAGE
kustomization/flux-system main@sha1:80299a36 False True Applied revision: main@sha1:80299a36This will provide you with information about the Flux resources and their current status.
Step 2: Clone the Git Repository
After Flux is up and running, the next step is to push new configurations to the git-ops repository for my-cluster.
Clone the fleet-infra repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/$GITHUB_USER/fleet-infra
cd fleet-infraStep 3: Add the tsb Repository to Flux

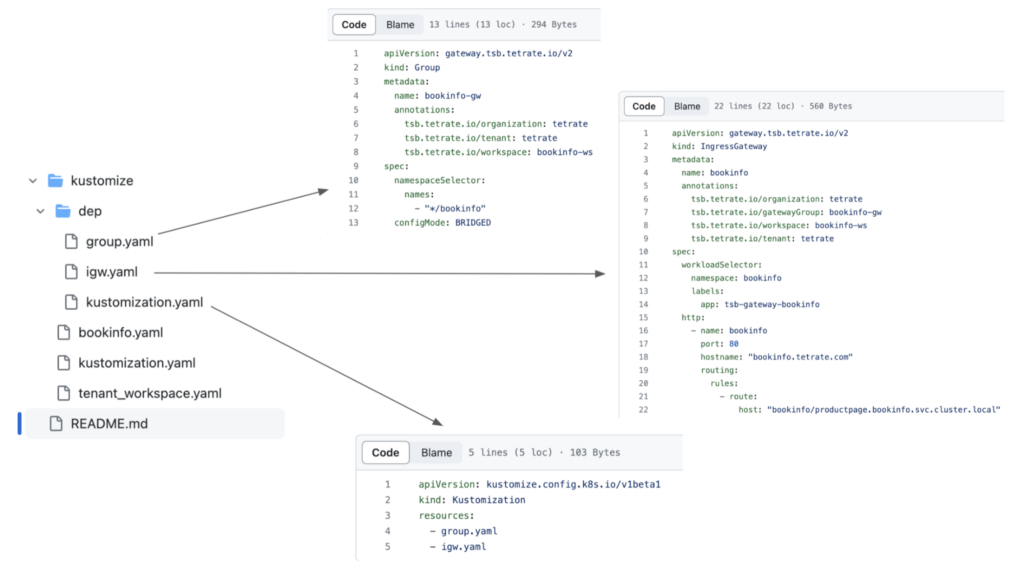

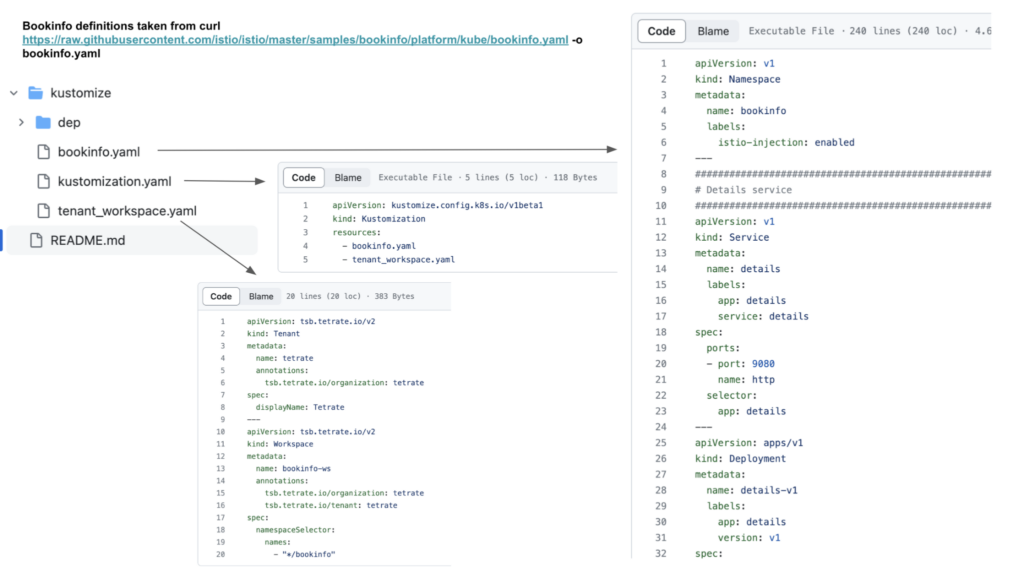

Note: bookinfo definitions can be taken from istio repository via curl [https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml -o bookinfo.yaml](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml) and TSB resources to be created from: Tenant, Workspace, Config Groups, Ingress Gateway respectively.
Step 3.1. Create a GitRepository manifest pointing to tsb repository’s master branch:
flux create source git tsb \
--url=https://github.com/<your-private-repo>/tsb \
--branch=master \
--interval=30s \
--export > ./clusters/my-cluster/tsb-bookinfo-source.yamlThe output should be similar to:
cat tsb-bookinfo-source.yaml
---
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: GitRepository
metadata:
name: tsb
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 30s
ref:
branch: master
url: https://github.com/<your-private-repo>/tsbStep 3.2. Commit and push the tsb-bookinfo-source.yaml file to the fleet-infra repository:
git add -A && git commit -m "Add bookinfo-source to GitRepository"
git pushStep 4. Deploy bookinfo Application and TSB Resources
Configure Flux to build and apply the kustomize directory located in the tsb repository.
Step 4.1. Use the flux create command as described in the steps below to create a Kustomization that applies the TSB deployment in the correct order. This will enforce a strict order when applying them into the cluster.
Step 4.1.1. Create bookinfo services:
flux create kustomization tsb \
--target-namespace=bookinfo \
--source=tsb \
--path="./kustomize" \
--prune=true \
--interval=2m \
--export > ./clusters/my-cluster/bookinfo-kustomization.yamlStep 4.1.2. Create TSB resources and their configuration based on the TSB resource hierarchy:
flux create kustomization tsb-dep \
--target-namespace=bookinfo \
--source=tsb \
--path="./kustomize/dep" \
--prune=true \
--interval=2m \
--depends-on=tsb \
--export >> ./clusters/my-cluster/bookinfo-kustomization.yamlThe output should be similar to:
cat bookinfo-kustomization.yaml
---
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: tsb
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 2m0s
path: ./kustomize
prune: true
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: tsb
targetNamespace: bookinfo
---
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: tsb-dep
namespace: flux-system
spec:
dependsOn:
- name: tsb
interval: 2m0s
path: ./kustomize/dep
prune: true
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: tsb
targetNamespace: bookinfoFrom the above output we can see that the second batch of deployments (tsb-dep) depends on the first one (tsb). This means that objects are configured in yaml files from path ./kustomize in the tsb private repo will be deployed first:
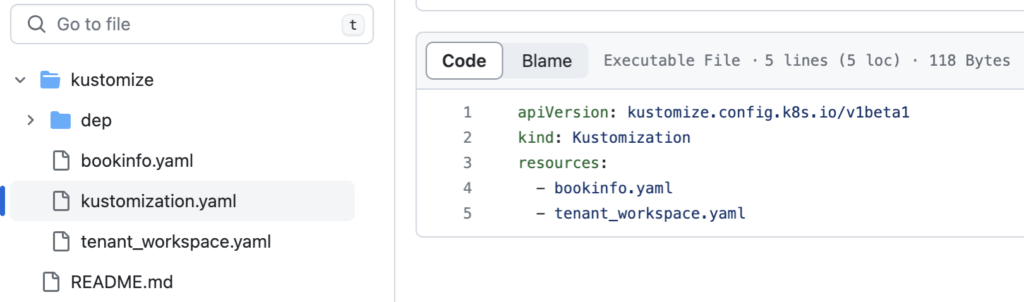

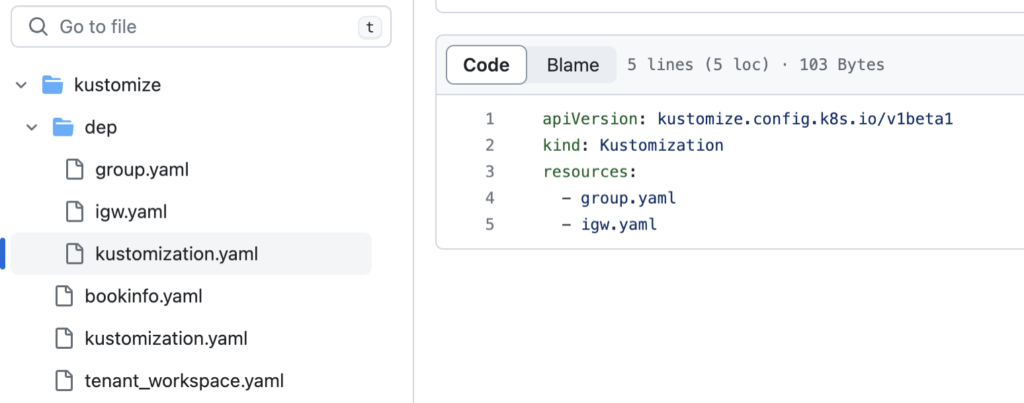
And objects are configured in yaml files from path ./kustomize/dep from the tsb private repo will be deployed after:

Step 4.2. Commit and push the Kustomization manifest to the repository:
git add -A && git commit -m "Add bookinfo-kustomization Kustomization"
git pushThe structure of the fleet-infra repo should be similar to:
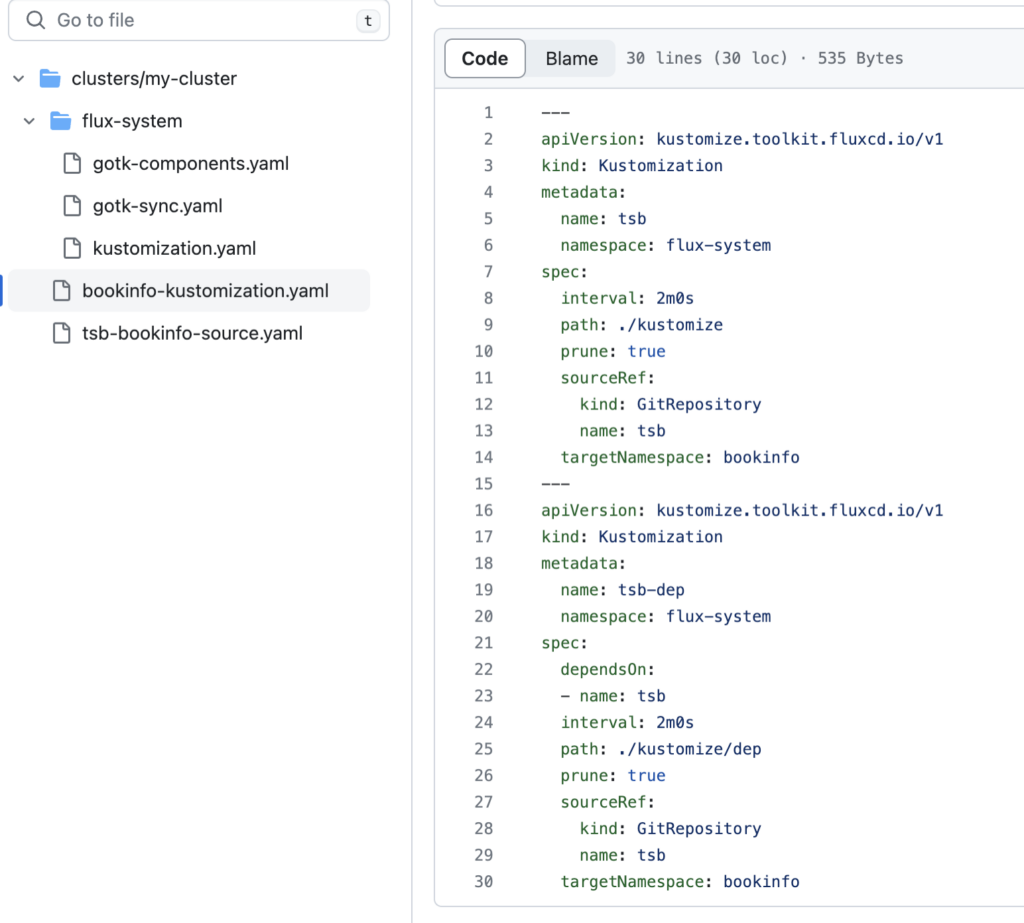

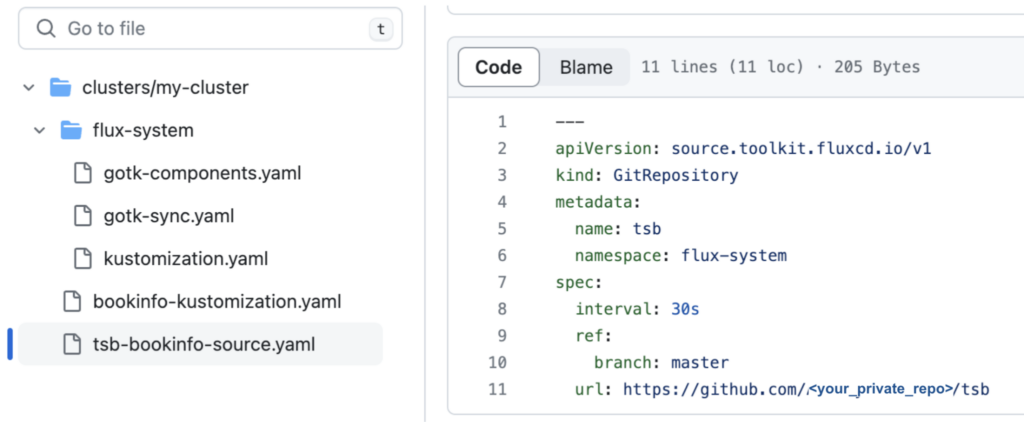

Step 5: Watch Flux Sync the Application and TSB Objects
Step 5.1. Use the flux get command:
flux get kustomizations --watchThe output should be similar to:
flux get kustomizations --watch
NAME REVISION SUSPENDED READY MESSAGE
flux-system main@sha1:a08dcaf9 False True Applied revision: main@sha1:a08dcaf9
tsb-dep master@sha1:98a10b48 False True Applied revision: master@sha1:98a10b48
tsb master@sha1:98a10b48 False True Applied revision: master@sha1:98a10b48Step 5.2. Check that the bookinfo application has been deployed on your cluster:
kubectl get all -n bookinfo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/details-v1-8567b4445b-9vt7c 2/2 Running 0 3d23h
pod/productpage-v1-6d5bff6746-mf9t2 2/2 Running 0 3d23h
pod/ratings-v1-7f8745548-49v62 2/2 Running 0 3d23h
pod/reviews-v1-6bb8f77d4c-hl5k4 2/2 Running 0 3d23h
pod/reviews-v2-86968c9c99-gndjh 2/2 Running 0 3d23h
pod/reviews-v3-6fffc5458c-xk2dx 2/2 Running 0 3d23h
pod/tsb-gateway-bookinfo-56b575bbdd-tnnfb 1/1 Running 0 3d23h
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/details ClusterIP 10.100.176.70 <none> 9080/TCP 3d23h
service/productpage ClusterIP 10.100.57.151 <none> 9080/TCP 3d23h
service/ratings ClusterIP 10.100.97.60 <none> 9080/TCP 3d23h
service/reviews ClusterIP 10.100.42.81 <none> 9080/TCP 3d23h
service/tsb-gateway-bookinfo LoadBalancer 10.100.143.153 lbdns.ca-central-1.elb.amazonaws.com 15443:31889/TCP,80:31659/TCP,443:31152/TCP 3d23h
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/details-v1 1/1 1 1 3d23h
deployment.apps/productpage-v1 1/1 1 1 3d23h
deployment.apps/ratings-v1 1/1 1 1 3d23h
deployment.apps/reviews-v1 1/1 1 1 3d23h
deployment.apps/reviews-v2 1/1 1 1 3d23h
deployment.apps/reviews-v3 1/1 1 1 3d23h
deployment.apps/tsb-gateway-bookinfo 1/1 1 1 3d23h
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/details-v1-8567b4445b 1 1 1 3d23h
replicaset.apps/productpage-v1-6d5bff6746 1 1 1 3d23h
replicaset.apps/ratings-v1-7f8745548 1 1 1 3d23h
replicaset.apps/reviews-v1-6bb8f77d4c 1 1 1 3d23h
replicaset.apps/reviews-v2-86968c9c99 1 1 1 3d23h
replicaset.apps/reviews-v3-6fffc5458c 1 1 1 3d23h
replicaset.apps/tsb-gateway-bookinfo-56b575bbdd 1 1 1 3d23h
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/tsb-gateway-bookinfo Deployment/tsb-gateway-bookinfo <unknown>/75% 1 10 1 3d23hStep 6: Validate TSB Configuration
Validate TSB objects have been deployed and configured as per tsb repo manifests using either the tctl CLI or the TSB web-based user interface.
Step 6.1: Review TSB Configuration with the tctl CLI
Step 6.1.1: Review the TSB tenant config with tctl:
tctl get tenant -oyaml
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
displayName: Tetrate
name: tetrate
organization: tetrate
resourceVersion: '"g/gDdysAnlQ="'
spec:
displayName: Tetrate
etag: '"g/gDdysAnlQ="'
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/tetrateStep 6.1.2: Review the TSB workspace config**:**
tctl get workspace bookinfo-ws -oyaml
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: bookinfo-ws
organization: tetrate
resourceVersion: '"1XSQLvmqJCM="'
tenant: tetrate
spec:
etag: '"1XSQLvmqJCM="'
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/tetrate/workspaces/bookinfo-ws
namespaceSelector:
names:
- '*/bookinfo'Step 6.1.3: Review the TSB gateway groups config:
tctl get gatewaygroups --tenant tetrate --workspace bookinfo-ws -oyaml
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
name: bookinfo-gw
organization: tetrate
resourceVersion: '"GFkG2plUAO0="'
tenant: tetrate
workspace: bookinfo-ws
spec:
etag: '"GFkG2plUAO0="'
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/tetrate/workspaces/bookinfo-ws/gatewaygroups/bookinfo-gw
namespaceSelector:
names:
- '*/bookinfo'Step 6.1.4: Review the TSB ingress gateway config**:**
tctl get IngressGateway --tenant tetrate --workspace bookinfo-ws --group bookinfo-gw -oyaml
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: IngressGateway
metadata:
group: bookinfo-gw
name: bookinfo
organization: tetrate
resourceVersion: '"+xXA00ZMAaU="'
tenant: tetrate
workspace: bookinfo-ws
spec:
etag: '"+xXA00ZMAaU="'
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/tetrate/workspaces/bookinfo-ws/gatewaygroups/bookinfo-gw/ingressgateways/bookinfo
http:
- hostname: bookinfo.tetrate.com
name: bookinfo
port: 80
routing:
rules:
- route:
host: bookinfo/productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local
workloadSelector:
labels:
app: tsb-gateway-bookinfo
namespace: bookinfoStep 6.2 (optional): Review TSB Configuration with the TSB Web UI
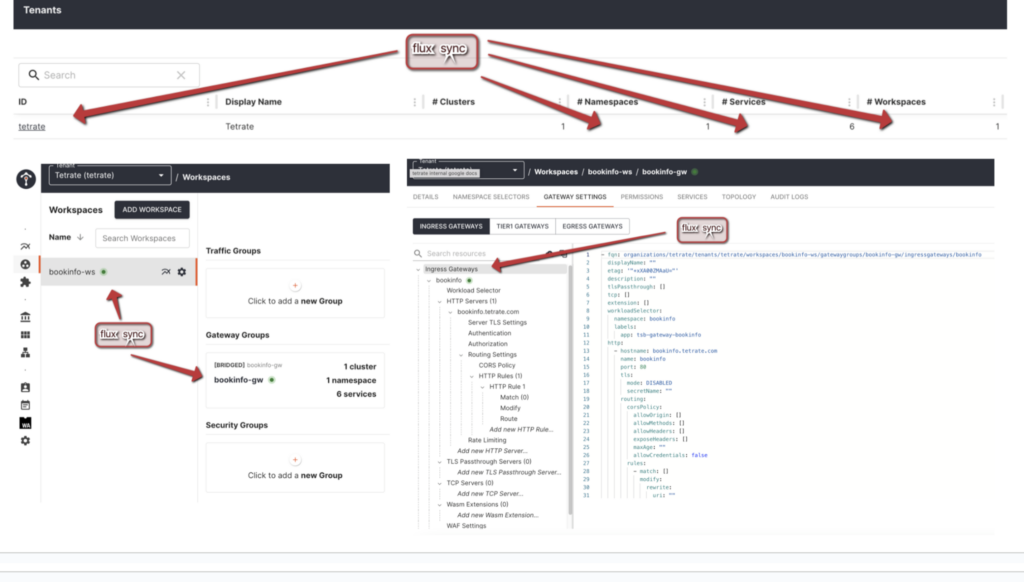

Changes made to the tsb manifests in the master branch are reflected in your cluster.
When a manifest is removed from the tsb repository, Flux removes it from your cluster. When you delete a Kustomizations from the fleet-infra repository, Flux removes all Kubernetes and TSB objects previously applied from that Kustomizations.
When you alter the bookinfo deployment using kubectl or edit TSB objects from the web UI or the tctl CLI, the changes will be reverted to match the state described in Git.
Conclusion
By configuring FluxCD for GitOps in conjunction with Tetrate Service Bridge, you can leverage the power of Git-based configuration management and automated synchronization combined with Tetrate’s global management plane to streamline service mesh configuration workflows.
This integration ensures consistency, traceability and automation in managing the TSB environment, allowing teams to focus on delivering more business value with less operational overhead. With the combined strengths of TSB, FluxCD and GitOps, organizations can simplify service mesh configuration while optimizing application deployment processes. By embracing this winning combination, organizations can unlock the full potential of their service mesh environments and accelerate their journey towards cloud-native excellence.










